Already purchased this program?
Login to View
This video program is a part of the Premium package:
- IEEE MemberUS $50.00
- Society MemberUS $0.00
- IEEE Student MemberUS $50.00
- Non-IEEE MemberUS $75.00
Renewables, Energy Storage and Power Electronics as Enabling Technologies for the Smart Grid Part II
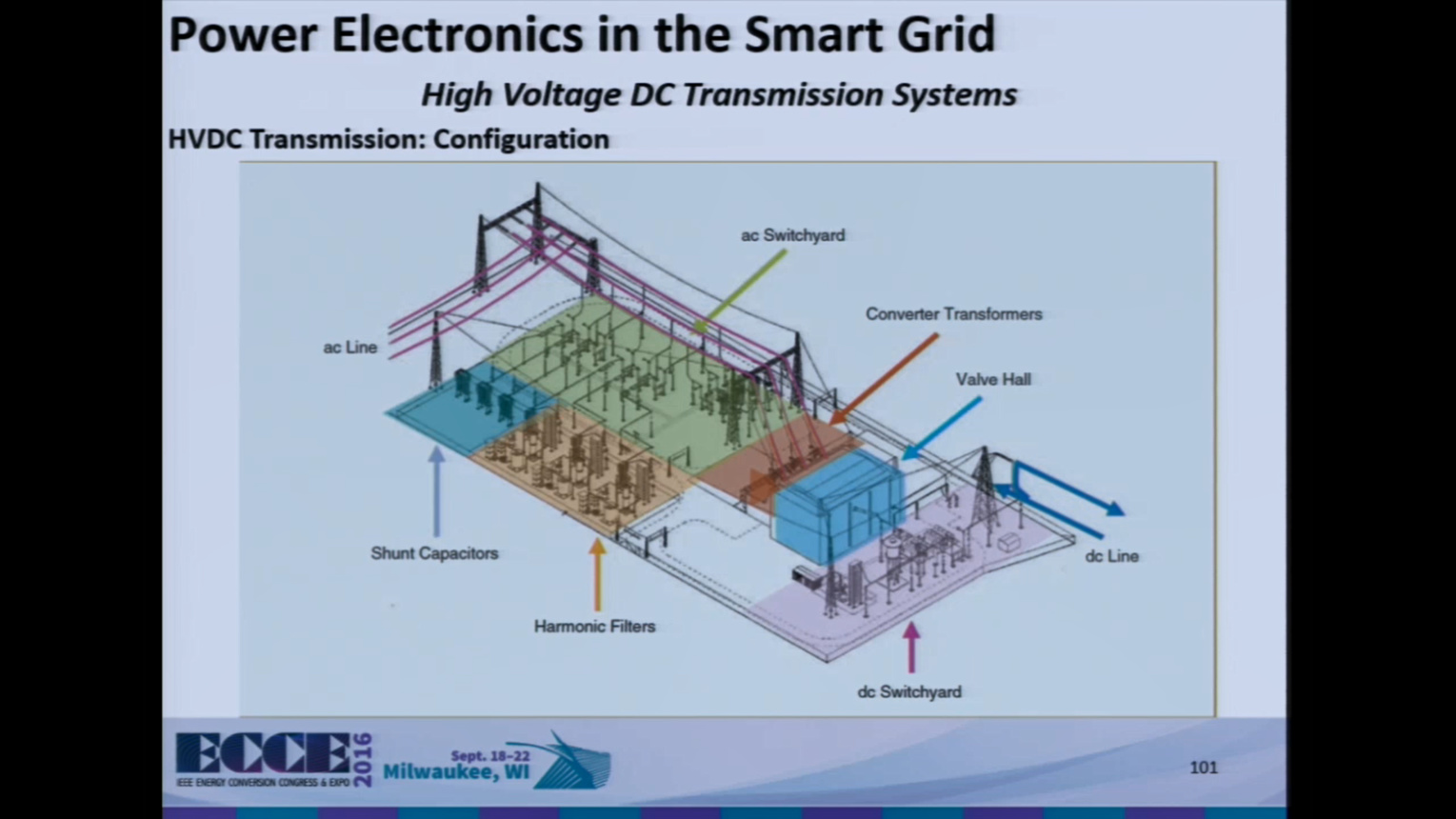
Instructors: Dr. Haitham Abu-Rub, Texas A&M University at Qatar Omar, USA, Dr. Omar Ellabban, Texas A&M University at Qatar Omar, USA The smart grid (SG) as a research area is advancing dealing with a wider range of topics such as power systems, energy generation and telecommunication. The conventional utility grid used to operate in a passive mode absorbing energy from the substations and delivering it to the customers. This approach is well developed but the needs of the state-of-the-art technology require a bidirectional flow of power and data. Nevertheless, smart grid systems provide more flexible, reliable, sustainable, secure and two- way communication service. Especially, integration of renewable energy sources, electrical vehicles and distributed generations (DG) in to network can be achieved in an efficient way in smart grid system. All these positive aspects of smart grids have been attained by integration of power electronics and telecommunication technologies with the grid. This presentation deals with contributions of power electronics to SG in the context of generation, conversion, and distribution.
Instructors: Dr. Haitham Abu-Rub, Texas A&M University at Qatar Omar, USA, Dr. Omar Ellabban, Texas A&M University at Qatar Omar, USA The smart grid (SG) as a research area is advancing dealing with a wider range of topics such as power systems, energy generation and telecommunication. The conventional utility grid used to operate in a passive mode absorbing energy from the substations and delivering it to the customers. This approach is well developed but the needs of the state-of-the-art technology require a bidirectional flow of power and data. Nevertheless, smart grid systems provide more flexible, reliable, sustainable, secure and two- way communication service. Especially, integration of renewable energy sources, electrical vehicles and distributed generations (DG) in to network can be achieved in an efficient way in smart grid system. All these positive aspects of smart grids have been attained by integration of power electronics and telecommunication technologies with the grid. This presentation deals with contributions of power electronics to SG in the context of generation, conversion, and distribution.
 Cart
Cart Create Account
Create Account Sign In
Sign In
